(MFOSC-P)

MFOSC-P presents a novel design and cost-effective way to develop a FOSC (Faint Object Spectrograph and Camera) type of instrument on a shorter time-scale of development. Its design and development methodology are, in particular, suitable for the small aperture telescopes. The design and other characterization aspects of MFOSC-P are discussed in the following reference:
“Design and development of Mt.Abu faint object spectrograph and camera – Pathfinder (MFOSC-P) for PRL 1.2m Mt. Abu Telescope”,
Srivastava et al., 2021, Experimental Astronomy, volume 51, pages345–382"
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10686-021-09753-5
Instruments Design Specifications
(from Srivastava et al. 2021, Experimental Astronomy, volume 51, pages345–382 ( https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10686-021-09753-5 ))
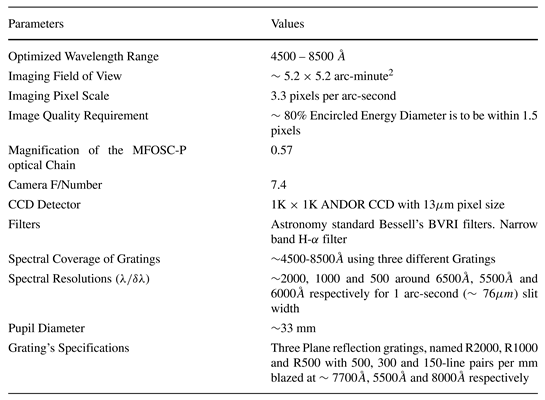
Gratings Specifications for Spectroscopy
(from Srivastava et al. 2021, Experimental Astronomy, volume 51, pages345–382 ( https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10686-021-09753-5 ))
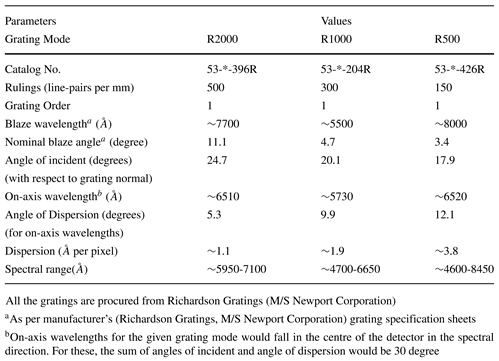
Emission line profiles from calibration lamps spectroscopy
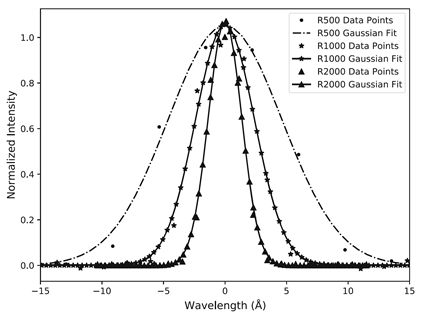
Figure 1: Figure shows the line profiles for Xenon and Neon spectral calibration lamps for all the three spectroscopy modes of MFOSC-P for 75 microns slit (~1 arc-second on the sky). The central zero wavelength corresponds to Xenon lamp’s 7119 angstrom line using R500 (150 lp/mm) grating (Dots), Xenon lamp’s 5028 angstrom line using R1000 (300 lp/mm) grating (stars), and Neon lamp’s 6506 angstrom line using R2000 (500 lp/mm) grating (triangles). Gaussian fits to these lines result in ∼3 pixels FWHMs which correspond to 10.9, 5.7 and 3.2 angstroms respectively for R500, R1000, and R2000 modes respectively. Figure is reproduced from Srivastava et al., 2021, Experimental Astronomy, volume 51, pages345–382.
MFOSC-P on-Sky Spectra of T CrB – A Symbiotic System
Figure 2: Spectra of a symbiotic system - T CrB as obtained from MFOSC-P from its three spectroscopy modes for varying resolutions and spectral ranges.
SNR achieved from MFOSC-P for Spectroscopy
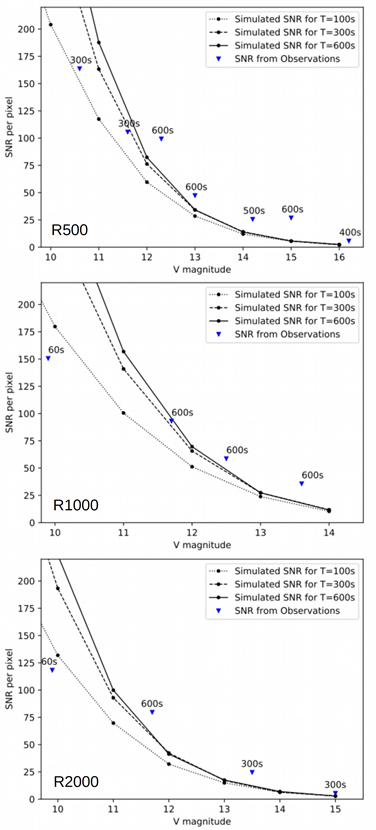
Figure 3: Comparison of simulated Signal to noise ratio (SNR) from MFOSC-P spectra with observed data. The model assumes 2.0 arc-seconds FWHM seeing and 1.0 arc-second slit width. Figure is reproduced from Srivastava et al., 2021, Experimental Astronomy, volume 51, pages345–382.
MFOSC-P on-Sky imaging
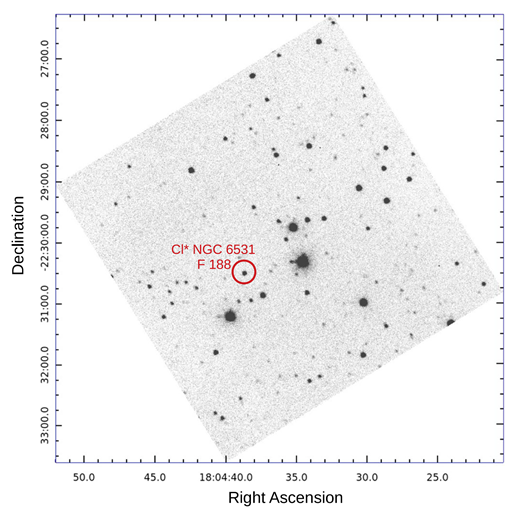
Figure 4: V band Image of a region of M21 Open Cluster from MFOSC-P. A source of V magnitude ∼15.74 (encircled) is observed with an error of 0.15 magnitude (SNR∼7.3) in 40 seconds of integration time. Figure is reproduced from Srivastava et al., 2021, Experimental Astronomy, volume 51, pages345–382.
Publications from MFOSC-P
Refereed Publications
- “A phenomenological study of the evolution of shock-induced O I emission lines in the spectrum of nova V2891 Cygni ”, Pandey et al., 2024, MNRAS, 532, 4, 3985-4001 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stae1719)
- “Intra-night optical variability of peculiar narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies with enigmatic jet behaviour”, Ojha et al., 2024, MNRAS: Letters, 529, 1, L108–L114 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnrasl/slae003)
- “Exploring the short-term variability of H α and H β emissions in a sample of M dwarfs”, Kumar et al., 2023, MNRAS, 524, 4, 6085–6101 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stad2222)
- “Optical and X-ray studies of Be/X-ray binary 1A 0535+262 during its 2020 giant outburst”, Chhotaray et al., 2023, MNRAS, 518, 4, 5089–5105 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stac3354)
- "Optical and near-infrared spectroscopy of Nova V2891 Cygni: Evidence for shock-induced dust formation", Kumar et al,2022, MNRAS, 510, 3, 2022, 4265-4283 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stab3772)
- “The Flare-Activity of 2MASSJ16111534-1757214 in the Upper Scorpius association”, Guenther et al, 2021, MNRAS, 507, 2, 2103–2114 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stab1973)
- “Design and development of Mt.Abu faint object spectrograph and camera - Pathfinder (MFOSC-P) for PRL 1.2m Mt. Abu Telescope”, Srivastava et al., 2021, Experimental Astronomy, 51, 345–382 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-021-09753-5)
- “UV spectroscopy confirms SU Lyn to be a symbiotic star”, Kumar et al., 2021, MNRAS:Letters, 500,1, L12-L16 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnrasl/slaa159)
- “First results from MFOSC-P: low-resolution optical spectroscopy of a sample of M dwarfs within 100 parsecs”, Rajpurohit et al., 2020, MNRAS,492,4,5844-5852 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/staa163)
Conference Proceedings
- “Optical Spectroscopy of 1A 0535+262 Before, During, and After the 2020 Giant X-ray Outburst”, Naik et al., 2024, Volume 93 - Année 2024 — No 2 - Proceeedings of the 3rd BINA Workshop on the Scientific Potential of the Indo-Belgian Cooperation (DOI: https://doi.org/10.25518/0037-9565.11829)
- “Exploring the short-term variability of H-alpha and H-beta emissions in a sample of M Dwarfs”, Kumar et al., 2022, Proceedings of the 21st Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun (CS21), Toulouse, France, 04-08 July 2022, Edited By Edited by A. S. Brun, J. Bouvier, P. Petit (DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7588979)
- “Design and development of Mt. Abu faint object spectrograph and camera-pathfinder (MFOSC-P) for PRL 1.2m Mt. Abu telescope, India”, Srivastava et al., 2018, Ground-based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy VII. Proceedings of the SPIE, 107024I (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2309306)